Is there a possible Link Between Periodontal Disease and Cancer?
What exactly is gum disease?
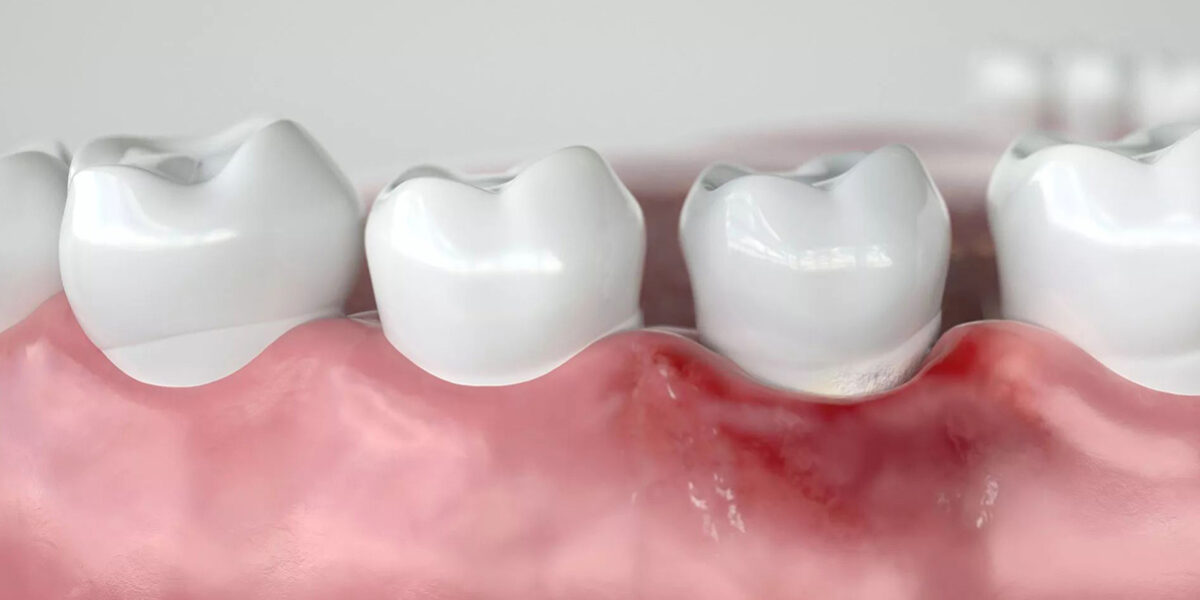
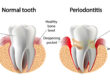
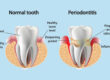
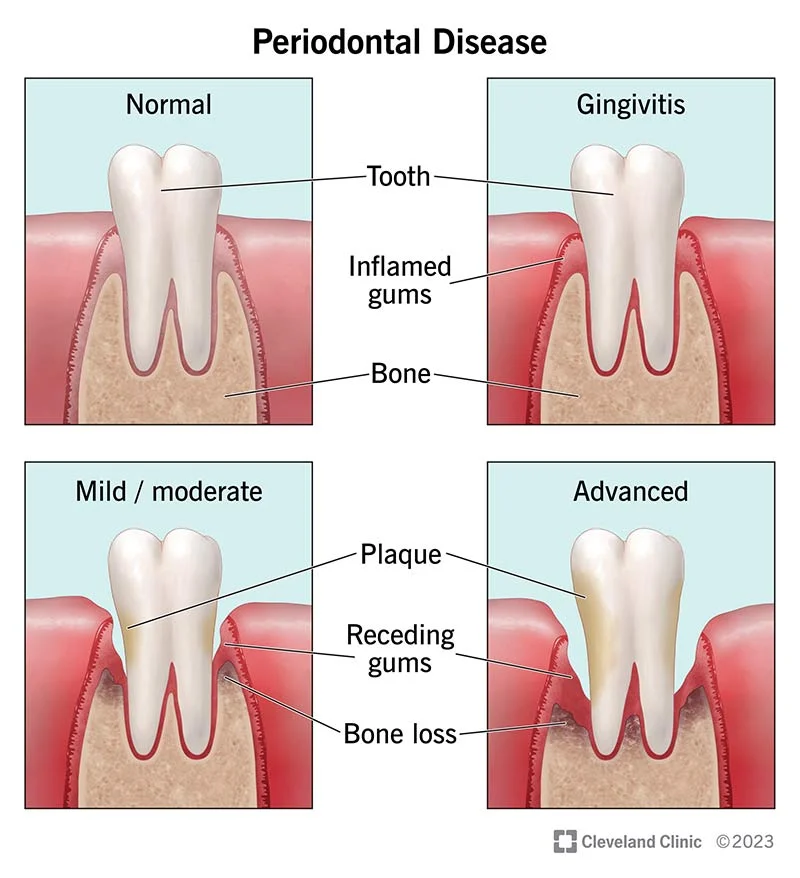
An persistent gum infection is brought on by the inflammatory condition known as periodontal disease. It can cause tooth loss by affecting the soft and hard dental support components. Periodontal disease develops once plaque has accumulated and hardened, which is frequently the result of bad brushing and flossing practices. There are four phases of periodontal disease, and only the first stage (gingivitis) is reversible, it’s crucial to note.
Gingivitis can progress to periodontitis if it is not treated. When a person has periodontitis, pockets occur when the inner layer of the gum and bone pulls away from the teeth. Infected debris can gather in these restricted areas. The immune system of the body battles the germs as the plaque spreads and increases below the gum line. The body’s infection-fighting enzymes and the toxins made by the bacteria in plaque at this stage begin to deteriorate the bone and connective tissue that support teeth. As the illness worsens, more bone and gum tissue are lost, and the pockets get deeper. When this occurs, teeth lose their ability to hold their positions and fall out.Gum Disease & Possible Cancer Risk Link
There has long been research linking periodontal disease to a higher risk of developing other inflammatory disorders. However, current studies suggest a possible link between some cancers and periodontal disease.
Inflammation, according to scientific theory, links systemic illnesses including metabolic syndrome, chronic renal disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and respiratory disease to periodontal disease. The rationale behind this was that, similar to how periodontal disease raises the risk of tooth decay, it also raises the risk of heart disease by causing plaque to accumulate in the arteries. Other studies are now revealing links between periodontal disease and particular types of cancer, like esophageal and stomach malignancies, even if this may still be the case.
What’s the connection to cancer risk?
Our mouths are home to a staggering number of good bacteria, collectively referred to as “oral biofilm.” These microorganisms produce pathogens that infect and irritate the gums when they are entrapped in plaque between the teeth. Toxins produced by pathogenic bacteria can enter your circulation. Your liver produces C-reactive proteins (CRP) as a result of your immune system’s response to infections and their poisons. Your body experiences chronic, low-grade inflammation as a result of the rise in CRP levels because it is constantly preparing to combat the infection.
Your body adapts to this increased inflammatory condition if periodontal disease is left untreated, which makes your immune system less active. Your immune system may experience irreparable harm over time, and this harm is thought to play a major role in the association between periodontitis and cancer. The precise relationship between the two illnesses is still unknown.
Recent discoveries
According to a long-term study published by Harvard in July 2020, those who have a history of periodontal disease are 43% more likely to get esophageal cancer and 52% more likely to develop gastric cancer than those with healthy gums. There may be a connection between oral health and esophageal and gastric cancers given that patients with these tumors also have dysbiotic oral microbiomes.
Why does this matter?
It’s crucial to remember that the Harvard study was observational and cannot establish a causal link between gum disease and cancer. Although more investigation is required, this finding may eventually lead to the inclusion of gum health in a patient’s total cancer risk assessment. Fortunately, maintaining proper oral hygiene and seeing a dentist regularly can avoid gum disease.
If you have any queries or worries concerning periodontal disease and its risks or or other disorders, we encourage you to Contact Us here at Oakstone Dental and discuss with our professional Dentists.