Top 8 indicators of tooth abscess
An accumulation of pus caused by a bacterial infection in the tooth’s pulp is known as a tooth abscess.
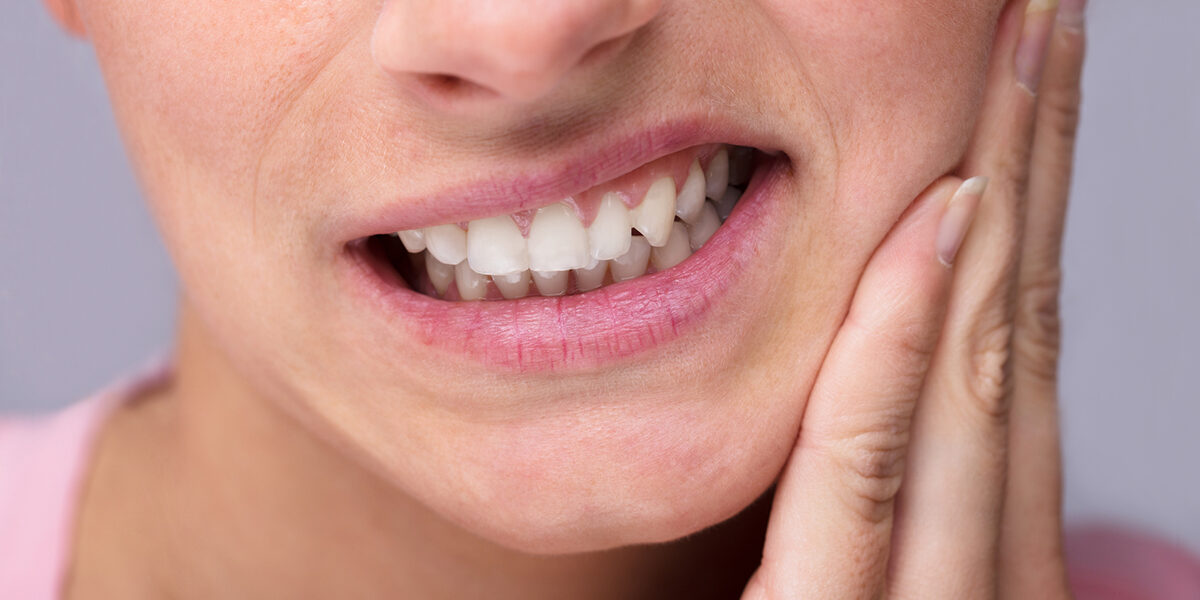
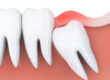
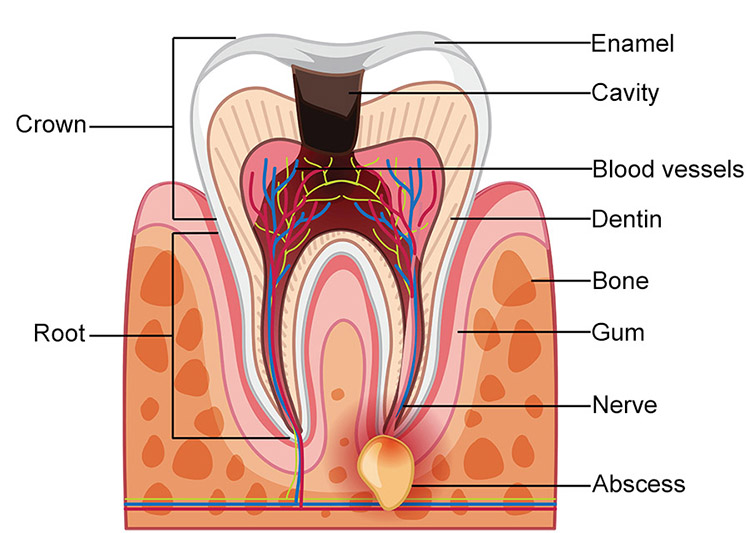
An accumulation of pus (dead tissue, live and dead bacteria, and white blood cells) and swelling of the tooth’s internal tissues are signs of infection. The result is an excruciating toothache.
Unless an abscess forms, the toothache may end if the tooth’s pulp dies. This is especially true if the infection is still present, spreading, and causing more tissue damage.
Symptoms
A terrible toothache is the predominant symptom. The ongoing discomfort can be described as throbbing, gnawing, acute, or shooting.
Causes, occurrence, and risk elements
A consequence of dental deterioration is a tooth abscess. Injuries to the teeth, as when one is fractured or chipped, may also cause it. Bacteria can enter the pulp of the tooth through cracks in the tooth enamel. The tooth’s root and the bones that support it may become infected as a result of an infection.
Other signs can include:
Unpleasant aftertaste
Breath smell
General unease, discomfort, or unwell feeling
Fever
Difficulty chewing
Teeth’s sensitivity to heat or cold
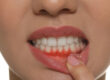
Gum swelling over the diseased tooth, which may resemble a pimple
Neck glands that are enlarged
Tests and signs
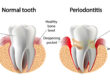
Your mouth, teeth, and gums will all be carefully inspected by the dentist. When the dentist taps the tooth, you could experience pain. Biting or tightly shutting one’s mouth also makes the discomfort worse. The gums could be swollen, red, and dripping with dense substance.
Your dentist can identify the tooth or teeth that are the problem with the aid of dental x-rays and other testing.
Treatment
Curing the infection, preserving the tooth, and avoiding sequelae are the objectives of treatment.
To treat the infection, antibiotics could be administered. Rinses in warm salt water might be calming. The toothache and fever may be relieved by over-the-counter painkillers.
Avoid applying aspirin directly to the tooth or gums as this will irritate the tissues more and raise the risk of mouth ulcers.
The tooth might need a root canal in an effort to preserve it.
If the infection is serious, the tooth may need to be extracted or surgery may be required to drain the abscess. It could be necessary to admit certain patients to the hospital.
Abscesses that are left untreated may worsen and develop potentially fatal consequences.
Infections are typically cured with prompt treatment. In most situations, the tooth can be salvaged.
Complications
Losing a tooth
Sepsis (blood infection)
infection that spreads to soft tissue (Ludwig’s angina, face cellulitis)
Osteomyelitis of the jaw is an infection that spreads to the jaw bone.
Infection spreading to different body parts and causing problems including pneumonia, endocarditis, or brain abscess
A highly dangerous symptom is a region of the upper or lower jaw that is swollen.
If you have a toothache that won’t go away or is throbbing, CONTACT US at Oakstone Dental for help